In the harsh environment of Antarctica, survival is a constant challenge for all living organisms. Recent research has shed light on an intriguing relationship between certain marine worms and bacteria that allows them to thrive in freezing temperatures. This symbiotic partnership provides valuable insights into the intricate balance of life in one of the harshest environments on Earth.
The Discovery of a Natural Antifreeze
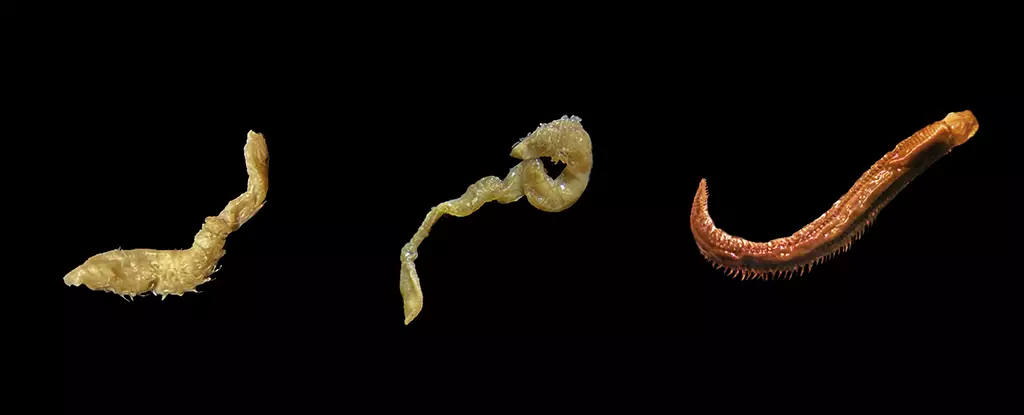
Researchers studying Antarctic marine worms have unraveled a fascinating discovery – some of these worms have formed relationships with bacteria that produce a natural antifreeze. The bacteria live inside the worms and secrete protein substances that protect against the icy water temperatures. This innovative adaptation allows the marine worms to survive in conditions that would otherwise be fatal.
The symbiotic relationship between the marine worms and bacteria is mutually beneficial. The bacteria produce chemicals such as proline and glycol, which lower the freezing point of the worms’ internal liquids, preventing ice formation within their cells. In return, the worms provide a hospitable environment for the bacteria to thrive. This intricate partnership highlights the interconnectedness of organisms in extreme environments.
The newfound knowledge of the Antarctic marine worms’ relationship with bacteria has the potential for practical applications, particularly in the field of cryopreservation. Understanding how these organisms adapt to freezing temperatures could provide valuable insights into preserving cells at low temperatures while keeping them alive. This research opens up possibilities for innovative approaches to cryopreservation techniques.
Beyond the realm of cryopreservation, the study of Antarctic marine worms and their bacterial partners offers a deeper understanding of the delicate balance of marine life in Antarctica. The adaptation mechanisms and cryo-resistance mediated by associated bacteria provide valuable insights into the complexities of survival in extreme environments. This research underscores the importance of maintaining the ecological balance in Antarctica, as increasing temperatures threaten the fragile ecosystem.
The unique relationship between Antarctic marine worms and bacteria illuminates the remarkable strategies that organisms employ to survive in harsh environments. This symbiotic partnership not only offers insights into adaptation mechanisms but also underscores the interconnected nature of life in Antarctica’s icy waters. Further research is needed to fully comprehend the longevity and impact of this relationship on the marine worms and their bacterial counterparts. The findings of this study open new avenues for exploring the mechanisms of adaptation and cryo-resistance in marine invertebrates, demonstrating the marvels of evolution in extreme conditions.

Leave a Reply